Designing Low Latency Segmentation Platform Using Upstash Kafka and MongoDB Connector
Introduction
- A segmentation platform plays a crucial role in understanding and categorizing customers, products, and other relevant data.
- Segmentation involves dividing a larger group into smaller, more homogeneous subgroups based on certain criteria.
- Here are a few examples of segmentation platforms in different domains, e.g., customer segmentation for personalized marketing strategies, targeted promotions, and a more customized shopping experience.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Requirements
- Basic Architecture
- Architectural Components
- Design Challenges
- Proposed Solutions
- Closing Notes
1. Understanding Requirements
Designing a low-latency segmentation platform for customer segments in e-commerce introduces specific challenges related to real-time processing, user experience, and the dynamic nature of customer behavior. Here are some challenges you might encounter in this context:
-
Large and Dynamic Datasets
- E-commerce platforms deal with large and constantly changing datasets, including customer profiles, product catalogs, and transaction histories.
- Managing and processing these vast datasets in real-time while maintaining low latency is a significant challenge.
-
Scalability
- Designing for scalability is essential to handle varying workloads. Ensuring that the system can scale horizontally by adding more processing units without sacrificing latency requires careful architecture planning.
-
Asynchronous Processing
- Leveraging asynchronous processing can help decouple components and improve overall system responsiveness. However, managing asynchronous communication without introducing complexities or delays requires careful design.
-
Data Flow and Pipelines
- Designing an efficient data flow and processing pipeline is crucial for low-latency systems.
- Minimizing the time data spends in transit between components and optimizing the sequence of processing steps can significantly impact overall latency.
-
Microservices Architecture
- Implementing a microservices architecture can enhance scalability and flexibility. However, ensuring seamless communication between microservices without introducing latency can be challenging.
- Designing efficient APIs and managing inter-service communication is critical.
2. Basic Architecture
The Segmentation Platform consists of three major subsystems:
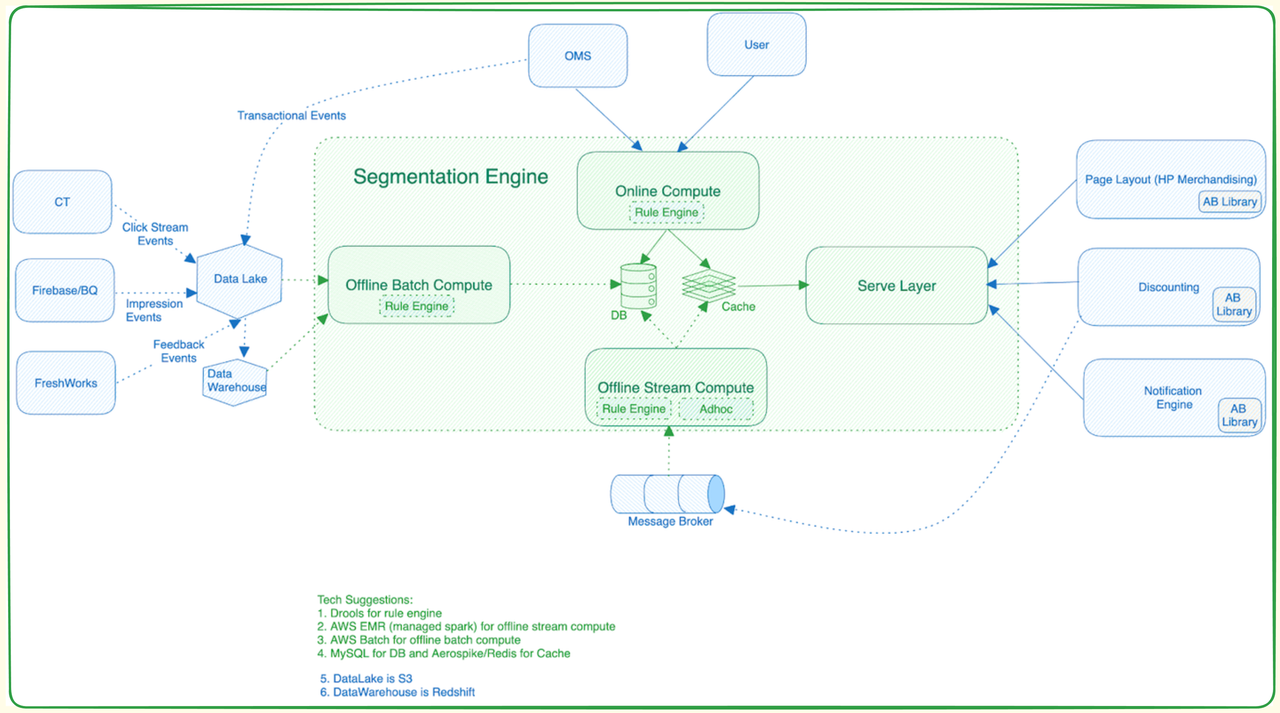
-
Compute Service (Offline Batch Compute/Online Compute):
- Extracts user segments from raw data using Spark Jobs.
- Spark job retrieves, cleans, and validates data from the data lake.
- Resulting data is sent to the serving sub-system.
-
Ingestion Service:
- Transfers calculated segments from the compute service to the segmentation service.
- Manages inclusion and exclusion of users within segments.
-
Segment Service (Serve Layer):
-
Provides user segments based on specific requirements for user service or discount service.
-
Discount service may query based on user ID and calculates available discounts
User ID Segment ID Created At 2521 Segment X Dec 3, 2023 2788 Segment Y Dec 3, 2023 3943 Segment Z Dec 3, 2023
-
3. Architectural Components
The Segmentation platform consists of following major components:
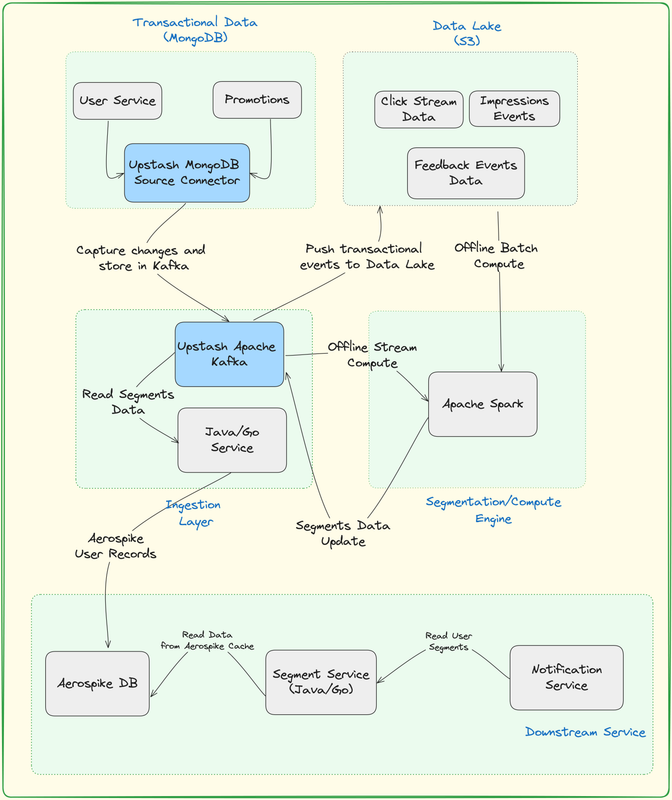
-
Data Lake - S3
- S3 is a widely adopted and versatile option for serving as a data lake. Its scalable and durable object storage capabilities make it suitable for efficiently storing and managing large volumes of diverse data types.
- By utilizing S3 as a data lake, organizations can benefit from its robust features for data storage, retrieval, and management, making it a popular choice in various data-centric applications and architectures.
-
Transactional Database MongoDB
- MongoDB's document-oriented model is beneficial for transactional use cases as it allows you to store complex data structures in a format similar to JSON. This flexibility is particularly useful for applications where the data structure might evolve over time.
-
Upstash Kafka Cluster
- You can stream the traffic (click) events from your web application to Upstash Kafka then you can store them to data lake for further processing.
- Upstash Kafka is the first Serverless Kafka offering. With a pay-per-request model, You can have a fully managed Kafka cluster without paying hundreds of dollars. With the free tier, You can create a Kafka cluster in seconds and without entering your credit card. The Upstash team takes care of availability, maintenance, scaling, upgrades and all the other tedious stuff while you focus on your app.
-
Upstash MongoDB Source Connector
- A MongoDB Source Connector is a component used in data integration and streaming platforms, such as Apache Kafka Connect, to connect to a MongoDB database and capture changes or events in real-time.
- Upstash MongoDB Source connector facilitates the movement of data from MongoDB to another system or platform, allowing for seamless data integration and analytics.
-
Apache Spark
- Apache Spark is a multi-language engine for executing data engineering, data science, and machine learning on single-node machines or clusters.
- By integrating Upstash Kafka with Apache Spark which is provided out of the box by Upstash, you will stream the traffic (click) events from your web application to Upstash Kafka then you can analyze it on real-time.
- Apache Spark will be responsible for processing updates to user segments. These updates will then be written to Upstash Kafka before being propagated to update the Aerospike database.
4. Design Challenges
The growing adoption and usage of the segmentation engine could potentially introduce certain challenges for the system.
- Write QPS Bottleneck: Creation of more and larger segments may lead to a bottleneck in write queries per second (QPS), resulting in prolonged wait times for segment creation.
- Lower Latency Request: Achieving very low latency is crucial for sending certain communications, especially when determining whether a user belongs to a specific segment.
-
Read Latency
-
Moreover, as the platform continues to evolve, even with the required < 50ms latency for reads, there is an anticipation that this speed might not be adequate for certain services and their future use cases.
-
For example, the notification service is expected to require rapid checks to determine user segment membership before sending out communications. Introducing increased latency for each communication request is anticipated to be unacceptable in the future.
-
-
Managing Kafka Infrastructure
-
Handling millions of events per minute from transactional sources can indeed pose challenges when using Kafka infrastructure, and the effective management of such a high throughput requires careful consideration of various factors.
-
Regular performance testing and optimization are key to maintaining a high-throughput Kafka infrastructure.
-
-
MongoDB Change Data Capture
-
Aggregating events from web applications, particularly when they are stored in traditional transactional databases like MongoDB, and then pushing them to a data lake can indeed involve some effort.
-
Utilize change data capture mechanisms provided by MongoDB or implement a custom solution to capture changes in the database.
-
5. Proposed Solutions
-
Distributed cache Aerospike to improve read latency
-
Aerospike will contain segments of a user where the user ID serves as the primary key for accessing user segments.
-
Additionally, you could also implement secondary indexes on segment IDs, streamlining the retrieval of segment users and eliminating the necessity of storing segment users separately
-
Furthermore, the design aims to meet latency requirements, with the potential for it to function as a cache, potentially replacing the need for Redis.
-
Replacing the current Aerospike with Upstash Redis would necessitate managing two sets of data: segment users and user segments.
-
-
Serverless Upstash Kafka to manage Kafka infrastructure
-
With Upstash Kafka, you get a completely managed service. This implies that Upstash handles all the technical tasks, such as server provisioning, scaling, and maintenance involved in running Kafka clusters.
-
This takes away the need for you to worry about things like setting up the infrastructure, getting everything to work correctly, and maintaining it over time.
-
This allows you to focus on leveraging Kafka for your unique requirements and objectives. Without the burden of managing infrastructure, you can now channel your energy into enhancing the overall quality of your application, particularly in a rapidly evolving development environment.
-
Price scales to zero: A true serverless offering shouldn't charge you if you're not actively using it. Price-per-request is our most outstanding feature. You've been designing your products and infrastructure to fit this pricing model from day one. This requires minimizing fixed costs, which is quite difficult for a beast like Kafka.
-
No operational burden for the user: The user creates the Kafka topic and starts using it. High availability, scalability, upgrades, backups… it's all our responsibility.
-
Connectionless: Serverless functions do not hold state. So you should be able to access your data with a stateless connection. Our Kafka offering supports the Kafka TCP protocol so all Kafka clients will work with Upstash. You also have a built-in REST API to enable connectionless environments like AWS Lambda or Cloudflare Workers.
-
-
MongoDB CDC using Upstash MongoDB Source Connector
-
Kafka Connect is a tool for streaming data between Apache Kafka and other systems without writing a single line of code. Via Kafka Sink Connectors, you can export your data into any other storage. Via Kafka Source Connectors, you can pull data to our Kafka topics from other systems.
-
Kafka Connectors can be self hosted but it requires you to setup and maintain extra processes/machines. Upstash provides hosted versions of connectors for your Kafka cluster. This will get the burden of maintaining an extra system from you and also it will be more performant since it will be close to your cluster.
-
6. Closing Notes
This blog post explores the design principles of a low-latency segmentation platform leveraging technologies provided by Upstash. The infrastructure is engineered to scale seamlessly, accommodating millions of users and handling terabytes of data stored in a data lake.
