Recently, we have observed many developers integrating Upstash with OpenAI and other AI APIs, such as Google Cloud AI, IBM Watson. Hugging Face. In this post, we will discuss the most common use cases and outline our future plans to support even more features.
Rate Limiting
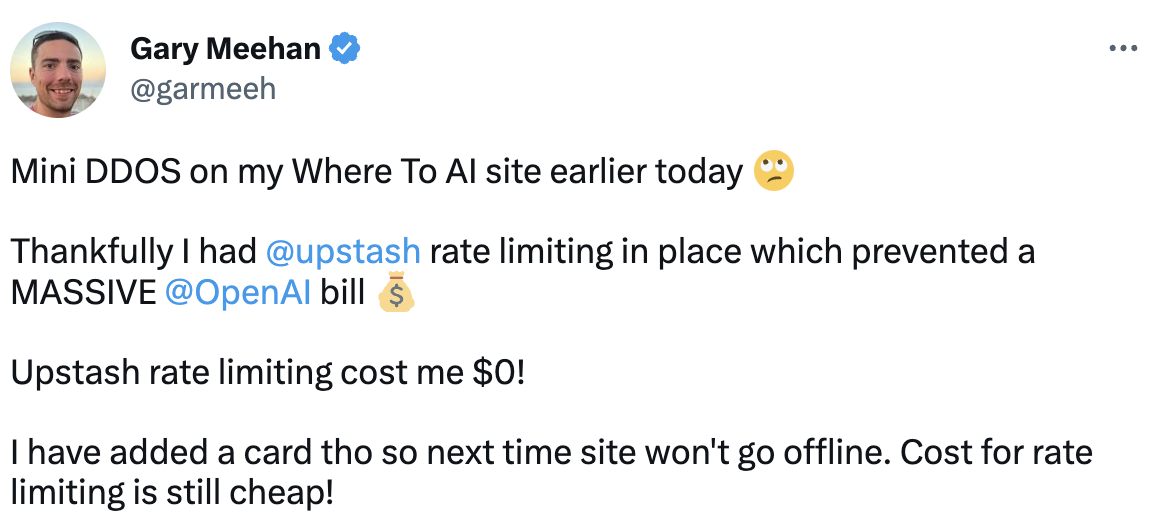
Rate limiting is a crucial component in managing AI-based applications, serving as a protective measure for both the developers and the users. As AI applications process large volumes of data and perform complex computations, they require significant computational resources. Without proper management, this could lead to system overloads, degraded performance, or even total system failure, leading to a poor user experience. Furthermore, rate limiting can act as a first line of defense against certain types of malicious attacks, such as DDoS attacks, which aim to overwhelm a system with traffic. Therefore, implementing rate limiting in AI applications helps maintain system stability, control costs, and enhance security.
Upstash offers an easy-to-use Rate Limit SDK that allows you to control how many requests can be made to your application in a time period. You can limit requests by IP address or user ID, and you can choose from a variety of algorithms, including fixed window, sliding window, and token bucket.
Asynchronous Processing
Asynchronous processing plays a pivotal role in the efficiency and performance of AI-based applications. These applications often have to handle large volumes of data and complex computations that can be time-consuming. When tasks are processed synchronously, or in sequence, the system must wait for each task to complete before starting the next, which can lead to significant delays and a poor user experience. This can be particularly troublesome for serverless applications, as increased processing times can inflate costs and potentially lead to timeout issues. In contrast, asynchronous processing allows multiple tasks to be executed concurrently, without having to wait for each task to complete.
QStash is a message queue designed for serverless applications that enables you to submit your API calls for asynchronous processing. QStash handles the API call and return the response to your specified callback.
Caching
Caching plays a vital role in the performance and efficiency of AI-based applications. Artificial Intelligence often involves computationally intensive tasks like training models, making predictions, or processing natural language, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. By implementing caching, an application can store the results of these operations and reuse them when the same operation is requested again, thereby avoiding the need to repeat the computation. Caching is an effective strategy for reducing the cost of expensive API calls.
Upstash Redis is an excellent solution for caching OpenAPI responses. By setting an expiration time on cached API calls, you can ensure that your application only consumes OpenAPI resources when a suitable cached response is unavailable or outdated.
Semantic Caching
A specialized caching use case for AI applications is prompt caching. Semantic caching can be very useful to increase efficiency and performance of AI based applications.
Semantic caching is different from traditional caching methods in that it stores the meaning of a query or request instead of just the raw data. This allows the cache to be more efficient, as it can be used to answer queries that are similar to previous queries, even if the exact query is not stored in the cache.
For example, if a user queries for "cars", the semantic cache could store the meaning of the query, such as "vehicles with four wheels and an internal combustion engine". This would allow the cache to answer queries for "automobiles", "motor vehicles", and "trucks", even if these queries are not stored in the cache.
Note: Redis Search module supports vector similarity queries but Upstash is not compatible with Redis Search. There is a project to implement similarity search to support semantic queries inside Upstash.
Example: Art Generator
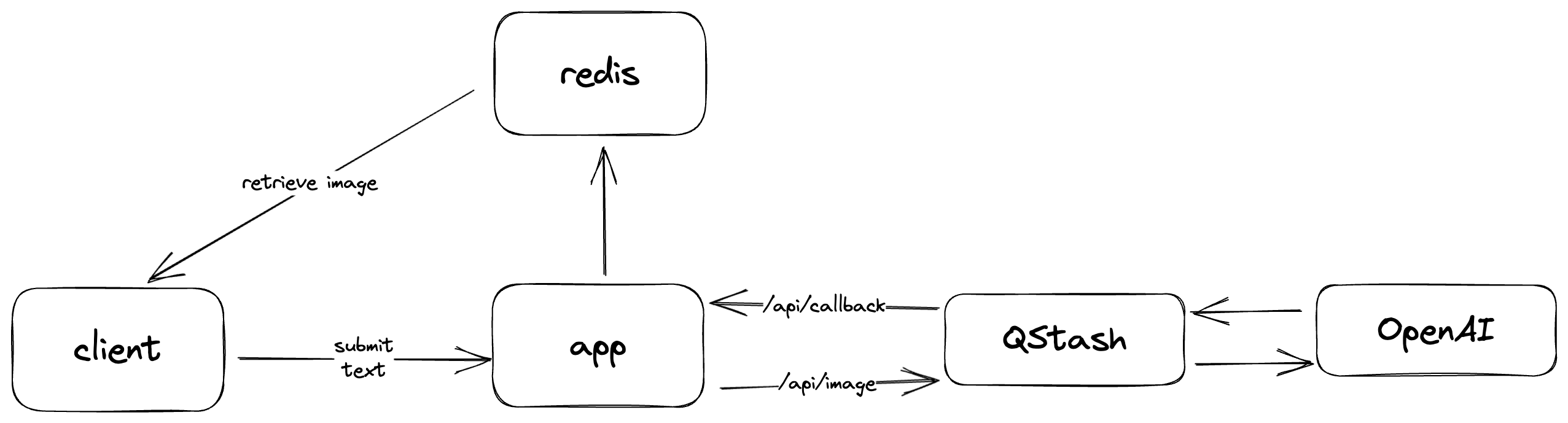
The Art Generator powered by Dall-E-2 uses AI to generate images from text and relies on Upstash Redis to cache the generated images. It also employs QStash to manage API calls and process them asynchronously, avoiding serverless function timeouts.
Upon receiving a text submission, the application sends the request to the OpenAI API via QStash's /api/image endpoint. QStash then gathers and forwards the response to /api/callback as a URL, which is subsequently stored in Upstash Redis. After invoking the OpenAI API, the client queries Redis and retrieves the image if it is available.
By delegating API call management to QStash, developers can avoid serverless function timeouts when deploying on Vercel's Hobby plan, which has a 10-second limit.
Example: RestorePhotos
RestorePhotos is an innovative application that restores old face photos using AI. As it gained popularity, the author implemented Upstash Redis to rate limit API usage, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Check here the code section where rate limiting is implemented.
Conclusion
As Upstash team, we are really impressed how developers adopt Redis to solve challenges while developing their application powered by AI. We have following plans to make their life better:
- Develop SDKs to ease the consumption of AI APIs as well as adding functionality of rate limiting, caching and async processing.
- Support semantic caching and similarity queries with either Redis Search API or a better API.
