Build an AI Assistant with Dify and Upstash
In this blog, we'll build an AI assistant using Dify AI and Upstash. This assistant can:
- Store content and search knowledge from uploaded files using Upstash Vector and Dify's file uploading
- Make Google searches and store search results to answer questions
- Rate-limit requests using Upstash Redis-based rate limiting for Dify
What is Dify AI?
Dify AI is an open-source visual AI builder that allows you to:
- Build AI applications with no or minimal coding
- Create workflows, chatbots, AI agents, chatflows, and text generators
- Use built-in plugins or develop your own
Dify integrates with OpenAI, Anthropic, and others - use whichever model you prefer for your app.
Application Overview
I'll show you how to build an AI assistant in Dify that:
- Accepts file uploads (PDFs, docs) and stores their content in Upstash Vector
- Allows users to run Google searches when their queries start with
SEARCH: - Rate-limits user requests using a custom Dify Plugin powered by Upstash Redis
- Responds to user queries using data retrieved from the vector database
You can build this entire app using:
- Dify's visual Chatflow builder
- The open-source Upstash Rate Limit Plugin
- HTTP blocks and Python Code blocks
Let's get started!
Step 1: Setting Up Dify
- Create an account on Dify AI
- Create a new Chatflow App
- Enable the File Upload feature under Features
- Start the Chatflow application with the following structure:
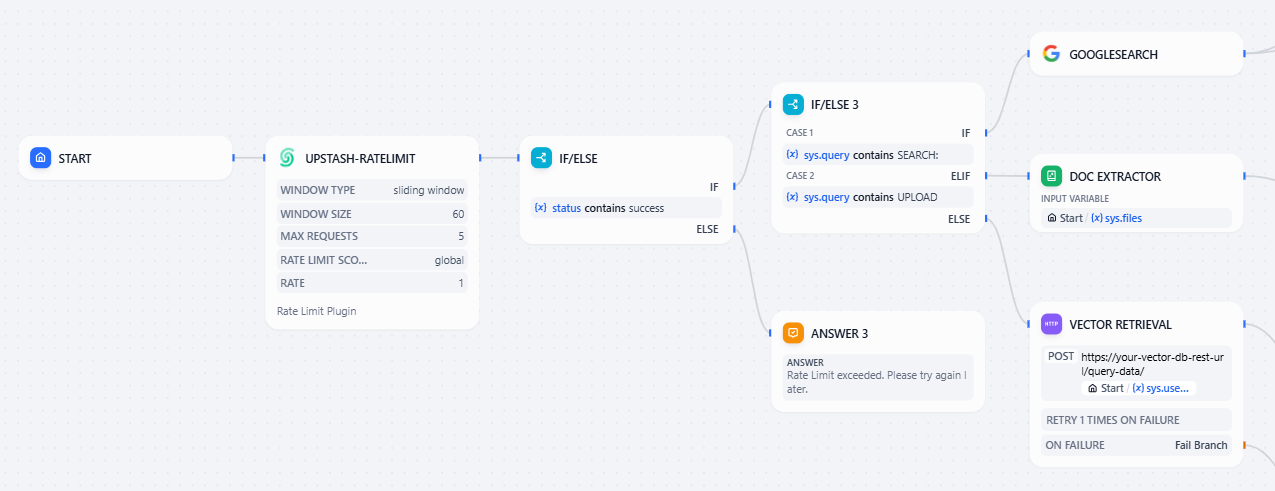
Step 2: Enable Rate Limiting with Upstash Plugin
I've developed and published a custom Dify Plugin that uses Upstash Rate Limiting. The code repository for the plugin can be found here.
Rate-Limiting Plugin Features:
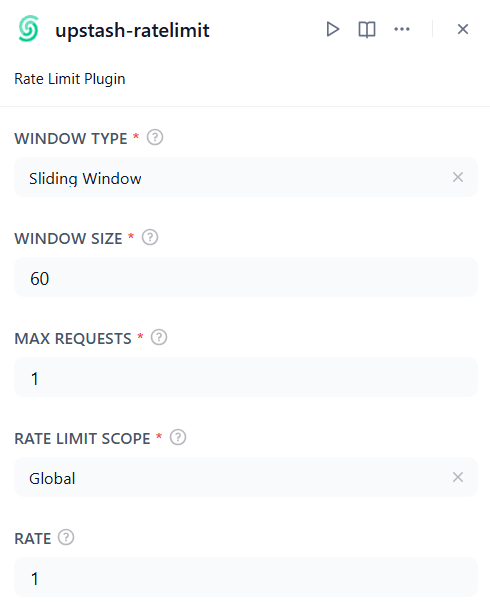
- Fixed or Sliding Window Rate Limiting
- Per-user or Global Scope
- Configurable max requests in a selected time interval (window size) and rate per request
How to Use:
- Install the plugin from the Dify Marketplace
-
Provide your
Upstash Redis REST URLandTokento authorize the plugin -
Add the plugin as the first step in your Chatflow and configure it for your application
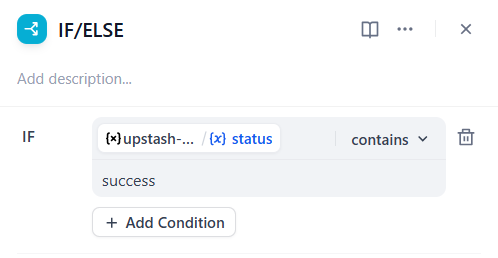
-
Add a follow-up
If-Elseblock to check if the rate limit is exceeded and check if the plugin status variable indicates success
This rate limit will prevent abusive traffic and provide fair usage across users.
You can use additional output variables to improve the application:

Step 3: Storing Uploaded Documents in Upstash Vector
If the user provides files to be uploaded:
- Extract the file contents using a document extraction tool
- Split the extracted text into chunks with a code block
# 👇 split to chunks
import requests
def main(text: str) -> dict:
chunks = [sentence.strip().replace('"', '').replace("\n", "") for sentence in text[0].split(".") if sentence.strip()]
return {
"result": chunks
}- For each chunk, we make an HTTP POST request to:
https://<your-upstash-vector-rest-url>/upsert-data/{{#sys.user_id#}}Using user_id in the URL creates a new namespace for each user and makes sure each user chats with their own assistant, not someone else's.
Add your REST TOKEN to the authorization section as a Bearer so you can perform requests.
- Send the following JSON body:
{
"id": "{{#sys.workflow_run_id#}}-{{#iteration.index#}}", // Provides a unique ID for each chunk
"data": "{{#iteration.item#}}",
"metadata": { "resource": "Doc Upload" }
}Overall, this branch will follow the below logic:
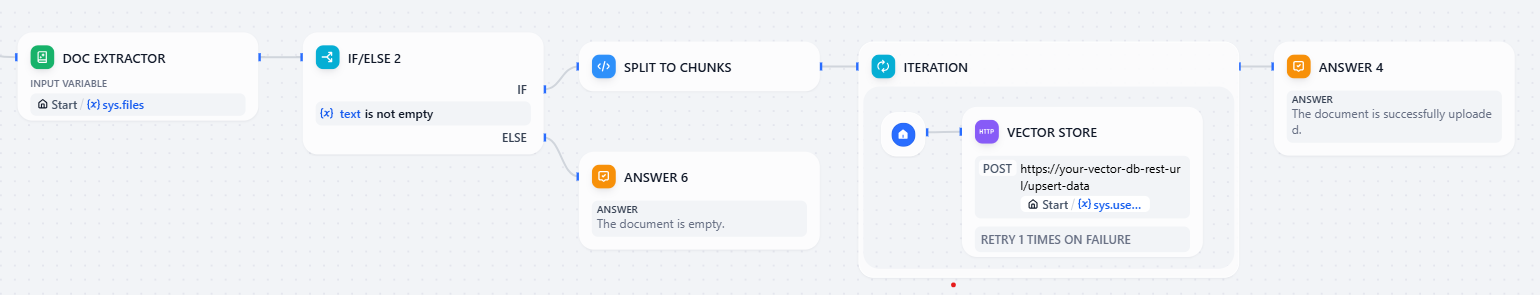
For the application to follow this logic, a user query needs to start with UPLOAD.
Step 4: Google Search Integration
I'll show you how to add a Google Search Plugin to:
- Let users search Google
- Take links and snippets from the search
- Store those results in the Upstash Vector Database
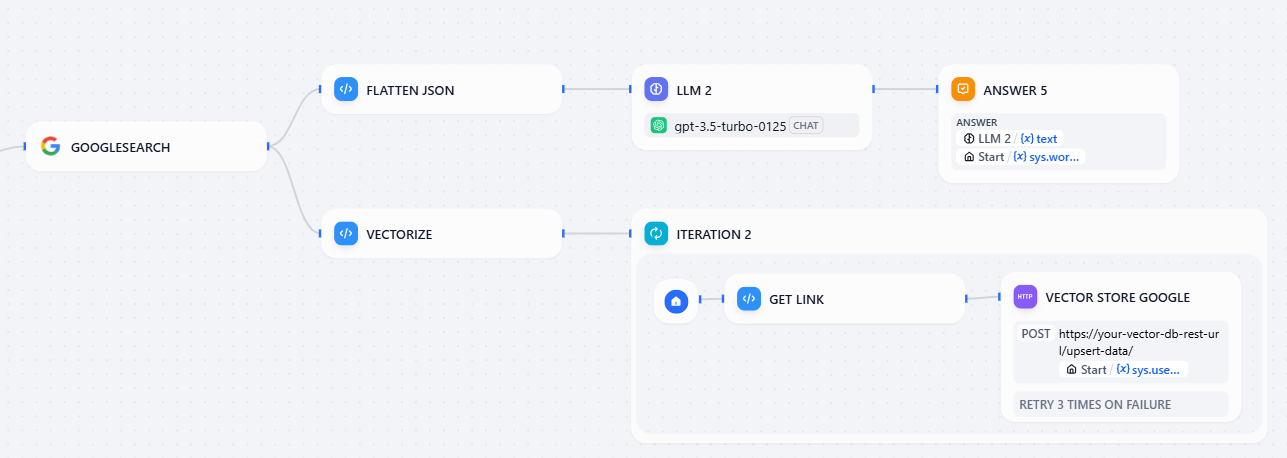
To perform a search:
- Users type a query like
SEARCH: what is Upstash? - A conditional block checks if the query starts with
SEARCH: - It routes to the search tool and then to the rest of the logic
Flatten JSON code block takes the Google search JSON result and returns them as a string named result. Then, LLM uses this formatted string to generate a response and passes it to the user.
# 👇 flatten json
def main(searchResult: list) -> dict:
formatted = []
for item in searchResult[0]["organic_results"]:
title = item.get("title", "No Title")
snippet = item.get("snippet", "No Snippet")
link = item.get("link", "No Link")
formatted.append(f"Title: {title}\nSnippet: {snippet}\nLink: {link}")
return {
"result": "\n---\n".join(formatted)
}The Vectorize code block splits search results into chunks, which are then upserted to the vector database using HTTP requests in the next iteration block.
def main(searchResult: list) -> dict:
if not searchResult or "organic_results" not in searchResult[0]:
return {"chunks": []}
chunks = []
for item in searchResult[0]["organic_results"]:
title = item.get("title", "")
snippet = item.get("snippet", "")
link = item.get("link", "")
if snippet:
content = f"{title}. {snippet} ({link})"
chunks.append(content.strip())
return {
"result": chunks
}Step 5: Knowledge Retrieval From Vector DB
When a user asks a question:
- Retrieve the relevant data from Upstash Vector using the
/query-dataendpoint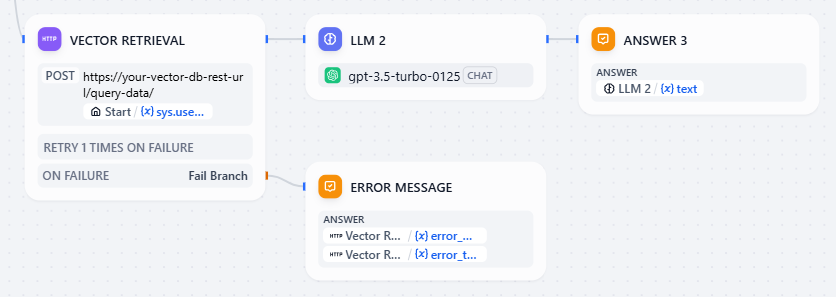
- Add
Content-Type: application/jsonto the Headers and add JSON body like the following:
{
"data": "{{#sys.query#}}", // user prompt
"top_k": 6, // determines how many vectors will be retrieved
"includeVectors": false,
"includeMetadata": true,
"includeData": true
}- Append them to your LLM context
- Let the LLM generate a final response
Our AI assistant combines knowledge from both file contents and search results to provide accurate answers.
Conclusion
- Upstash Rate-Limit Plugin handles traffic control for fair usage and protects your app from overload
- Upstash Vector Database enables your assistant to learn and recall user-provided documents and search results over time
- Dify allows you to orchestrate complex AI logic visually, with almost zero backend code
With this setup, you're not just building a chatbot; you're creating an AI assistant that learns from user input and customizes its responses. Upstash handles both chat memory and rate-limiting, while Dify orchestrates the business logic.
Following this tutorial, you can build your AI assistants in minutes with Dify + Upstash.
